
The client then encodes the message using the key, a new IV and sends it to the AP.
#JAVASCRIPT GET MAC ADDRESS OF WLAN ACCESS POINT GENERATOR#
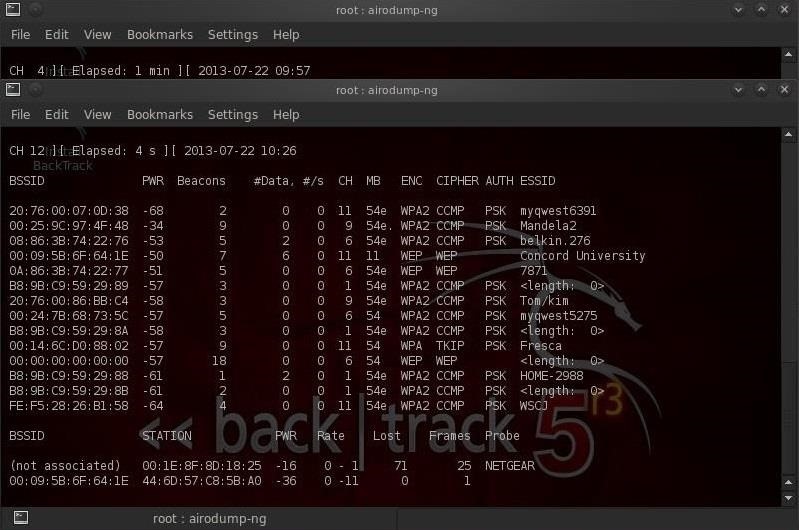
The client sends a authentication request indicating the use of a shared key The AP responds with a challenge containing 128 Octets generated with the WEP pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) seeded with the shared key and an initialization vector (IV). Open systems may also employ MAC access lists to determine if the AP responds with an authorization success frame.ġ1 WEP Association WEP relies on a shared key There are 3 association states 1)Unauthorized and unassociated 2)Authenticated and unassociated 3)Authenticated and associated To move from state1 to state 2 in an open system, a client sends a authentication request, and the AP responds with an authorization success frame. The SSID is required for all communication with an access point.ġ0 Association Before a client can communicate with the AP, a relation or association must be established.
Supposed to give the same amount of privacy as a wired LAN Used to prevent eavesdropping Used to prevent unauthorized access to the LAN (not explicitly a goal of WEP)Īpplication Application SSL SSL Transport (TCP, UDP) Transport (TCP, UDP) Router Network (IP) Network (IP) Network (IP) Network (IP) (VPN) (VPN) 802.11b Link 802.11b Link Ethernet Link Ethernet Link WEP WEP 802.1b Physical 802.1b Physical Ethernet Physical Ethernet PhysicalĨ Beacon Frame Each access point broadcasts a beacon frame several times a second It contains: The beacon interval – How often does the frame get broadcast A time stamp Service Set Identifier (SSID) Supported transmission rates Parameter sets – frequency hops, delay, etc Compatibility info – such as: all clients must use WEP Traffic Map – What AP are in power saver modeĩ Probe Frame A client may broadcast a probe frame to find the AP associated with an SSID. When an access point is found, a chalk mark is placed on the sidewalk or building Called the Basic Service Set (BSS)ĥ War Driving & Chalking People drive around looking for access points. Wireless LAN Physical LAN has defined borders Wireless is difficult to determine where access stops Both are vulnerable to attacksĢ Standard 802.11 IEEE family of specifications for WLANs 2.4GHz 2Mb/s Includes WEP 802.11a 5GHz, 54Mb/s 802.11b Often called Wi-Fi, 2.4GHz, 11Mb/s 802.11e QoS & Multimedia support to b & a 802.11g 2.4GHz, 54Mb/s 802.11i An alternative of WEP, known as WPA2Ĭommunication only to computers within transmission range If communication to the internet is required then one of the members must act as a router Called the Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS)Įach client sends its data to an access point The access points acts as a bridge and forwards the packets to other clients or to the wired network. Wireless Local Area Network Extension of a wired LAN Uses high frequency radio waves (RF) Speed: 2 MB/s to 54 Mb/s Distance:100 feet to 15miles Physical vs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
